|
|
11 lat temu | |
|---|---|---|
| examples | 11 lat temu | |
| .gitignore | 11 lat temu | |
| Makefile | 11 lat temu | |
| README.md | 11 lat temu | |
| matplotlibcpp.h | 11 lat temu |
README.md
matplotlib-cpp
This is matplotlib-cpp, probably the simplest C++ plotting library. It is built to resemble the plotting API used by Matlab and matplotlib.
Usage
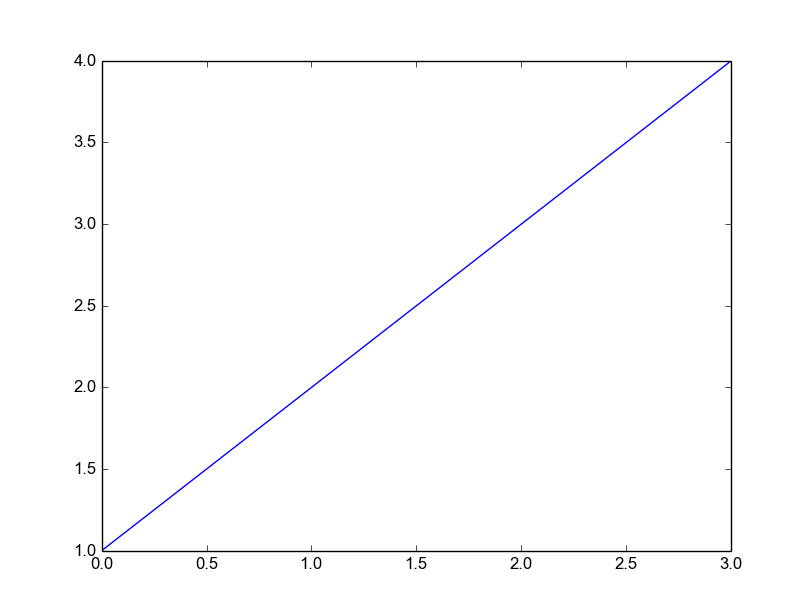
Complete minimal example:
#include "matplotlibcpp.h"
namespace plt = matplotlibcpp;
int main() {
std::vector<double> v {1,2,3,4};
plt::plot(v);
plt::show();
}
// g++ minimal.cpp -std=c++11 -lpython2.7
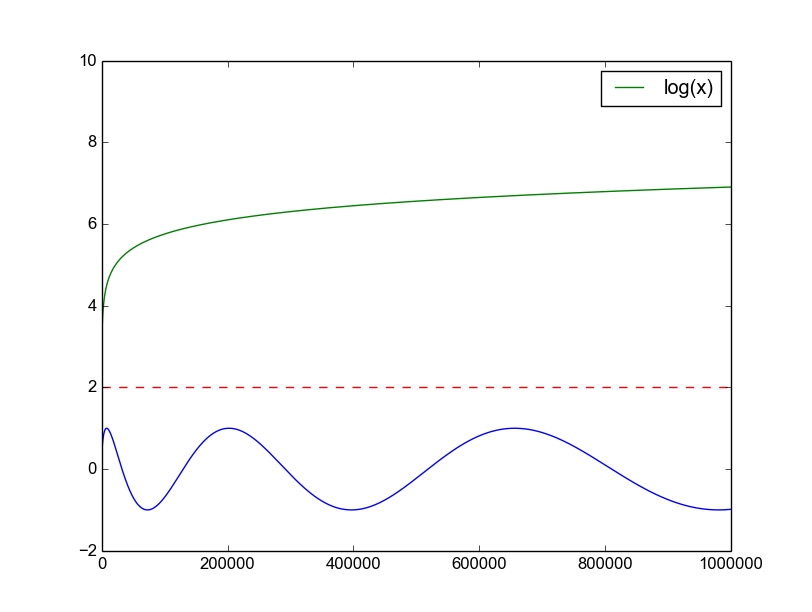
A more comprehensive example:
#include "matplotlibcpp.h"
#include <cmath>
namespace plt = matplotlibcpp;
int main()
{
// Prepare data.
int n = 5000;
std::vector<double> x(n), y(n), z(n), w(n,2);
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
x.at(i) = i*i;
y.at(i) = sin(2*M_PI*i/360.0);
z.at(i) = log(i);
}
// Plot line from given x and y data. Color is selected automatically.
plt::plot(x, y);
// Plot a red dashed line from given x and y data.
plt::plot(x, w,"r--");
// Plot a line whose name will show up as "log(x)" in the legend.
plt::named_plot("log(x)", x, z);
// Set x-axis to interval [0,1000000]
plt::xlim(0, 1000*1000);
// Enable legend.
plt::legend();
// Show plot
plt::show();
}
Installation
matplotlib-cpp works by wrapping the popular python plotting library matplotlib. (matplotlib.org) This means you have to have a working python installation, including development headers. On Ubuntu:
sudo aptitude install python-matplotlib python2.7-dev
The C++-part of the library consists of the single header file matplotlibcpp.h which can be placed anywhere. Since a python interpreter is opened internally, it is necessary to link against libpython2.7 in order to use matplotlib-cpp. (There should be no problems using python3 instead of python2.7, if desired)
Todo/Issues/Wishlist
It would be nice to have a more object-oriented design with a Plot class which would allow multiple independent plots per program.
Right now, only a small subset of matplotlibs functionality is exposed. Stuff like xlabel()/ylabel() etc. should be easy to add.